Lupine Publishers | Journal of Pediatric Dentistry
Abstract
The present study showed the presence of Candida tropicalis as a mayor fungus isolated of dental caries in deciduous teeth.
Keywords: Dental Caries, C Tropicalis
Introduction
Candida species is the most frequent fungus found in the oral cavity [1]. This microorganism provokes a pathology known as candidiasis in many forms [2], however, this yeast can be found in dental decay lesions, gingival and periodontal disease [3]. Candida albicans is the most frequent species of microorganism in all these lesions [4], however, other Candida species as Candida tropicalis, C glabrata, C. Krusei, C. guillermondii are less present in oral cavity [5]. Dental caries, is the most frequent lesions over world and its etiology is eminently microbial, being the Streptococcus mutans who produce the teeth demineralization and destruction [6]. The main of this study is to isolate and characterize the Candida species from dental caries in deciduous teeth.
Materials and Methods
Fifty children, female and male, from pediatric dentistry of Universidad Andina del Cusco, between 4 and 6 years old with dental caries are selected. Before remove and rehabilitate the dental caries, with a dental spoon excavator it was collected a caries sample and stored in 0.9% NaCl [7]. After that, the samples were sonicated and 100 ul aliquot was placed in CHROM Agar Candida medium (CHRO Magar, Paris, France) and were incubated for 48 hours at 37°C [7]. It followed the CHRO Magar Candida manual instructions to determine the presence of Candida species.
Results
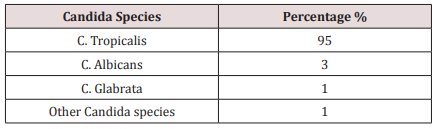
The Candida species most present in the dental caries in deciduous teeth were the C. tropicalis. Other species of Candida are found in less percentages (Table 1).
Discussion
Candida species is the most fungus found in oral cavity being the C Albicans the most pathological yeast of the Candida species [4]. This microorganism was found in many oral lesions as candidiasis, dental caries, gingival and periodontal disease [2,3]. Other Candida non albicans are founded in less frequency. However, C. tropicalis and C. glabrata has been described as emerging pathogens in recent years [8]. In the present study, C. tropicalis was presented in the most cases of dental caries in deciduous teeth, being this data corroborated with other studies who the main pathogen is the C. tropicalis. Most studies, in fact, found that the C. albicans as the mayor pathogen isolated from dental caries [6,9,10]. This difference of data can be explained by the geographical location of patients where Candida species can be found in amounts depending on the geographical area. In this study, other Candida species, can be found in less amounts. Despite limitations, the data obtained in the present study demonstrated the high rate of C. Tropicalis in dental caries in deciduous teeth, however, has not been determined which factor is involved in the pathogenesis of dental caries produced by C. tropicalis. It is also important study the oral microbiome in dental caries to dilucidated the role of Candida species, mainly C. tropicalis, in the development of dental caries in deciduous teeth.
Conclusion
Candida tropicalis is the most fungi founded in dental caries lesion in deciduous teeth in child between 4 and 6 years old.
Read More Lupine Publishers
Pediatric Dentistry Journal Articles:
https://lupine-publishers-pediatric-dentistry.blogspot.com/

No comments:
Post a Comment